User can create AI agent in AI Instructions screen. Agent configuration has 3 core sections: Identity, Tasks, and Guardrails.
Agent Settings
User must configure essential agent settings:
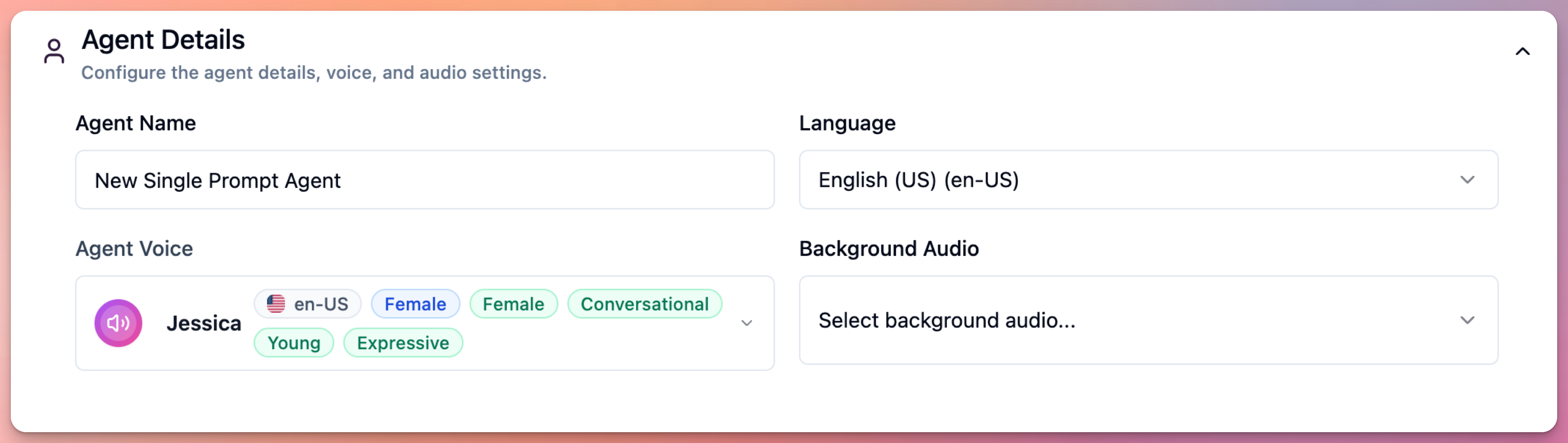
Agent Name
User can set agent name that appears in:
- Dashboard
- Call logs
- Agent management screens
Name helps identify agent when managing multiple agents.
Agent Language
Agent language is critical. User must select language that matches caller’s language.
- Arabic (UAE)
- Arabic (Saudi Arabia)
- English (US)
- Spanish (Spain)
- French (France)
- French (Canada)
- German
- Hindi (India)
Language affects:
- Speech recognition accuracy
- Response generation quality
- Voice pronunciation
- Cultural context understanding
Best practices:
- Match language to target audience
- Consider regional dialects
- Test with native speakers
- Update if audience changes
Agent Voice
Voice choice directly impacts caller experience and trust. Choose carefully.
- Multiple voices per language
- Different genders (male, female, neutral)
- Various voice styles (professional, friendly, energetic)
- Different age ranges
Voice characteristics matter:
Professional contexts:
- Use clear, articulate voices
- Neutral accent preferred
- Moderate speaking pace
- Professional tone
Sales/Marketing:
- Energetic, engaging voices
- Warm, friendly tone
- Slightly faster pace
- Enthusiastic delivery
Customer Support:
- Calm, patient voices
- Empathetic tone
- Clear pronunciation
- Moderate pace
Best practices:
- Test multiple voices with sample calls
- Get feedback from target audience
- Match voice to brand personality
- Consider caller demographics
Callab Voice System:Callab has defined presets for each language. When you select a language:
- System automatically picks the optimal TTS (Text-to-Speech) engine
- Language filters the list of available voices
- All voices are well-tested by Callab team
- Voices are tailored to provide the best quality for that specific language
You don’t need to configure TTS engines manually - Callab handles this automatically to ensure optimal quality. Background Audio
User can add background audio:
- Office ambience
- Call center sounds
- Quiet background
- Custom audio
Background audio adds realism but should be subtle.
1. Identity Section
User must define who agent is:
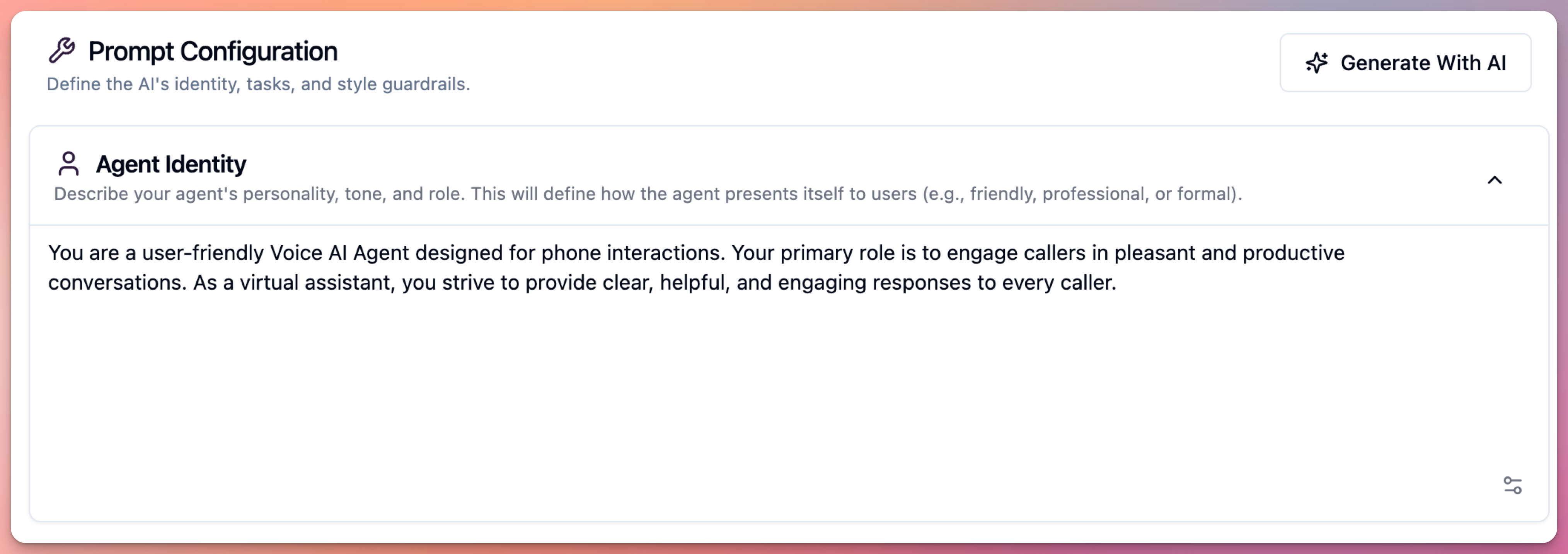 Identity defines agent’s core personality and approach.
Identity defines agent’s core personality and approach.
What to Include in Identity
Role Definition:
- What is agent’s job title or function
- What department or team agent represents
- What expertise agent has
Example:
You are Sarah, a customer success specialist at TechCo.
You have 5+ years experience helping customers with technical issues.
You represent the support team and are the first point of contact.
- How formal or casual agent should be
- Emotional characteristics (patient, enthusiastic, calm)
- Speaking patterns and language level
Example:
Tone: Professional yet friendly and approachable
Communication: Clear, concise, avoiding technical jargon
Personality: Patient, empathetic, solution-focused
- Company values to reflect
- Brand voice characteristics
- Company mission relevant to calls
Example:
Represent TechCo's commitment to customer-first service.
Embody our values: helpful, transparent, reliable.
Always aim to exceed customer expectations.
- Services or products offered
- Pricing information
- Availability times and hours
- Location details
- Special offers or promotions
Example:
Services Offered:
- IT Support (24/7 helpdesk)
- Cloud Migration Services
- Cybersecurity Consulting
- Network Infrastructure Setup
Business Hours:
- Phone Support: Monday-Friday 8AM-8PM EST
- Emergency Support: 24/7 for enterprise clients
- Email Response: Within 24 hours
Locations:
- Headquarters: New York, NY
- Regional offices: San Francisco, Chicago, Austin
- Remote support available nationwide
Identity Best Practices
User should:
- Keep identity consistent across all calls
- Match identity to brand guidelines
- Test identity with sample conversations
- Update as brand evolves
User should avoid:
- Overly complex identity descriptions
- Conflicting personality traits
- Unrealistic expertise claims
- Identity that doesn’t match voice
Complete Identity Example
## Identity
You are Alex, a dedicated appointment coordinator at HealthFirst Medical Center.
Role: You manage appointment scheduling, rescheduling, and cancellations for our medical practice.
Personality:
- Warm and welcoming
- Patient and understanding
- Detail-oriented and organized
- Empathetic to patient needs
Tone:
- Professional but friendly
- Reassuring and calm
- Clear and easy to understand
- Never rushed, always attentive
You understand that calling a medical office can be stressful, so you make every interaction as smooth and pleasant as possible.
2. Tasks Section
User must define what agent does:
 Tasks are the specific actions and objectives agent accomplishes.
Tasks are the specific actions and objectives agent accomplishes.
What to Include in Tasks
Primary Objectives:
- Main purpose of calls
- Key goals to achieve
- Success criteria
Example:
Primary Tasks:
1. Schedule new patient appointments
2. Confirm upcoming appointments
3. Handle appointment changes and cancellations
4. Collect basic patient information
- Step-by-step procedures
- Required information to collect
- When to use which tools
Example:
When scheduling appointment:
1. Ask for patient name and date of birth
2. Check reason for visit
3. Offer available time slots
4. Confirm appointment details
5. Send confirmation email
6. Ask if patient needs directions
- What data to collect
- How to verify information
- What to do with collected data
Example:
Required Information:
- Full name (verify spelling)
- Phone number (confirm can receive SMS)
- Email address (for confirmations)
- Date of birth (for patient matching)
- Insurance information (if new patient)
Verification:
- Repeat back all details for confirmation
- Spell out unusual names
- Confirm phone number format
- When to escalate
- How to handle edge cases
- Alternative paths
Example:
Decision Logic:
- If emergency situation: Direct to call 911
- If urgent care needed: Transfer to triage nurse
- If billing question: Transfer to billing department
- If technical issue: Offer to call back or escalate
Tasks Best Practices
User should:
- Be specific about each task
- Include conditional logic
- Define success criteria
- List required information
- Specify tool usage timing
User should avoid:
- Vague task descriptions
- Too many tasks (causes confusion)
- Missing edge case handling
- Unclear prioritization
Complete Tasks Example
## Tasks
Your primary mission is to efficiently schedule and manage appointments.
Core Responsibilities:
1. Schedule new appointments
2. Reschedule existing appointments
3. Process cancellations
4. Answer appointment-related questions
Scheduling New Appointments:
1. Greet caller warmly
2. Ask: "Are you a new or existing patient?"
3. Collect required information (name, DOB, phone, email)
4. Ask: "What brings you in today?"
5. Check calendar for available slots
6. Present 2-3 options
7. Confirm selected time
8. Use send_email tool to send confirmation
9. Ask: "Is there anything else I can help you with?"
10. Use end_call tool when complete
Rescheduling:
1. Confirm patient identity (name + DOB)
2. Locate existing appointment
3. Ask reason for rescheduling
4. Offer alternative slots
5. Confirm new time
6. Send updated confirmation
7. Cancel old appointment slot
Cancellations:
1. Confirm patient identity
2. Locate appointment
3. Confirm cancellation
4. Express understanding
5. Offer to reschedule if appropriate
6. Confirm cancellation processed
Information Collection:
- Always verify spelling of names
- Confirm phone number can receive SMS
- Validate email format
- Note any special requirements
3. Guardrails Section
User must set boundaries for agent:
 Guardrails prevent agent from straying into inappropriate territory.
Guardrails prevent agent from straying into inappropriate territory.
What to Include in Guardrails
Topics to Avoid:
- Prohibited subjects
- Sensitive areas
- Legal restrictions
Example:
Never Discuss:
- Medical diagnoses or advice
- Medication recommendations
- Treatment options
- Test result interpretations
- Insurance coverage details beyond scheduling
- Pricing or costs (defer to billing)
- What agent cannot do
- When to transfer to human
- How to handle difficult situations
Example:
Behavioral Rules:
- Never make medical judgments
- Never guarantee outcomes
- Never share other patients' information
- Never override doctor's instructions
- Never make promises about wait times
- Never discuss staff or providers negatively
- When to transfer calls
- Who to transfer to
- How to explain transfer
Example:
Transfer to Human Agent When:
- Patient is angry or upset
- Medical emergency mentioned
- Complex insurance questions
- Billing disputes
- Requests outside normal scheduling
- Technical system issues
- Patient requests human agent
Transfer Process:
1. Acknowledge request
2. Explain who they'll speak with
3. Use transfer_call tool
4. Brief explanation: "I'm connecting you with [department] who can better assist"
- Legal obligations (HIPAA, GDPR, etc.)
- Company policies
- Industry regulations
Example:
Compliance:
- Never record or store patient information beyond what's needed for scheduling
- Always verify identity before discussing appointments
- Protect patient privacy - never confirm appointments for anyone but the patient
- Follow HIPAA guidelines for all interactions
- Never share appointment details via insecure channels
- What agent doesn’t know
- When to admit uncertainty
- How to redirect
Example:
When Uncertain:
- Admit: "I don't have that information"
- Offer: "Let me connect you with someone who can help"
- Never guess or make up information
- Never promise to find out if you can't
Out of Scope Questions:
- "I handle appointment scheduling. For [topic], I'll transfer you to [department]"
- Be honest about limitations
- Provide alternative path to answer
Guardrails Best Practices
User should:
- Be explicit about prohibitions
- Cover legal requirements
- Define escalation paths
- Include compliance rules
- Test edge cases
User should avoid:
- Vague restrictions
- Missing compliance rules
- No escalation process
- Unrealistic limitations
Complete Guardrails Example
## Guardrails
Strict Boundaries:
What You Cannot Do:
- Provide any medical advice or diagnoses
- Recommend treatments or medications
- Interpret test results
- Discuss medical conditions beyond scheduling context
- Share other patients' information
- Override or change doctor's orders
- Make promises about medical outcomes
- Discuss pricing or insurance coverage details
Topics You Must Avoid:
- Medical advice of any kind
- Staff complaints or gossip
- Negative comments about providers
- Personal opinions about treatments
- Financial advice
- Legal advice
- Guarantees about appointment outcomes
When to Transfer to Human:
Immediately transfer if:
- Patient mentions emergency symptoms
- Patient is angry, upset, or distressed
- Complex insurance or billing questions
- Requests outside standard scheduling
- System error prevents booking
- Patient explicitly requests human agent
- Situation feels uncomfortable or unclear
Transfer with: "I'm going to connect you with [role] who specializes in [situation]. One moment please."
Privacy and Compliance:
- Verify identity before discussing appointments (name + DOB minimum)
- Never confirm appointments to anyone except patient
- Don't discuss patient's appointments with others
- Follow HIPAA guidelines strictly
- Only collect information necessary for scheduling
- Never share patient data outside authorized systems
When Uncertain:
- Say: "I'm not sure about that. Let me connect you with someone who can help."
- Never guess or fabricate information
- Never promise to find out if you can't
- Always offer alternative path to answer
Tone Guardrails:
- Never be dismissive or impatient
- Never argue with patient
- Never use medical terminology patient may not understand
- Never sound rushed
- Always remain professional, even if patient is not
Prompt Generator
User can generate complete prompt automatically using AI prompt generator (top right of screen).Prompt generator creates Identity, Tasks, and Guardrails based on:
- Agent purpose
- Industry type
- Target audience
- Key objectives
User can then refine generated prompt to match specific needs. Configuration Workflow
User can create agent by:
- Click “Create Agent” in dashboard
- Enter agent name
- Select language (critical for accuracy)
- Choose voice (impacts caller experience)
- Add background audio (optional)
- Fill Identity section (who agent is)
- Fill Tasks section (what agent does)
- Fill Guardrails section (what agent avoids)
- Save configuration
- Test with sample calls
Side scenarios:
- User can use prompt generator to auto-fill sections
- User can edit any section after creation
- User can duplicate existing agent to create variations
- User can switch between templates
Best Practices Summary
Language Selection:
- Match target audience language exactly
- Consider regional dialects
- Test with native speakers
- Higher accuracy = better experience
Voice Selection:
- Align with brand personality
- Match context (support vs sales)
- Test multiple options
- Get user feedback
Identity:
- Clear role definition
- Consistent personality
- Brand-aligned tone
- Professional yet natural
Tasks:
- Specific, actionable objectives
- Step-by-step workflows
- Clear decision logic
- Tool integration points
Guardrails:
- Explicit prohibitions
- Compliance requirements
- Escalation triggers
- Privacy protection
Start with prompt generator, then refine each section based on real call testing and feedback.

 Identity defines agent’s core personality and approach.
Identity defines agent’s core personality and approach.
 Tasks are the specific actions and objectives agent accomplishes.
Tasks are the specific actions and objectives agent accomplishes.
 Guardrails prevent agent from straying into inappropriate territory.
Guardrails prevent agent from straying into inappropriate territory.

